If your website isn’t ranking on Google’s first page, you’re losing potential customers every single day. The difference between position #1 and position #10 can mean thousands of visitors and significant revenue. But here’s the problem: Google uses over 200 ranking factors, and many website owners focus on outdated strategies that no longer work.
In 2026, Google’s algorithm has evolved dramatically. Traditional tactics like keyword stuffing and buying backlinks will get you penalized. Instead, Google now prioritizes user experience, content expertise, and genuine value delivery. This comprehensive guide reveals the exact ranking factors that matter right now and shows you how to optimize for each one.
Whether you’re struggling with low traffic, poor rankings, or wondering why competitors outrank you, this guide provides actionable solutions. You’ll learn which factors to prioritize, which mistakes to avoid, and how to build a sustainable SEO strategy that works in 2026 and beyond.
Understanding How Google Ranking Factors Work

Google’s ranking algorithm evaluates your website across multiple dimensions before deciding where to position it in search results. These ranking factors aren’t weighted equally—some carry significantly more influence than others.
The algorithm analyzes three core areas: content quality and relevance, technical performance and user experience, and authority and trustworthiness. Every factor within these categories sends signals to Google about whether your website deserves to rank higher or lower.
Here’s what makes 2026 different: Google’s AI-powered systems, particularly through Search Generative Experience (SGE) and AI Overviews, now understand context, user intent, and content quality at unprecedented levels. This means surface-level optimization won’t work anymore. You need genuine expertise, comprehensive coverage, and exceptional user experience to compete.
E-E-A-T: The Foundation of Content Quality
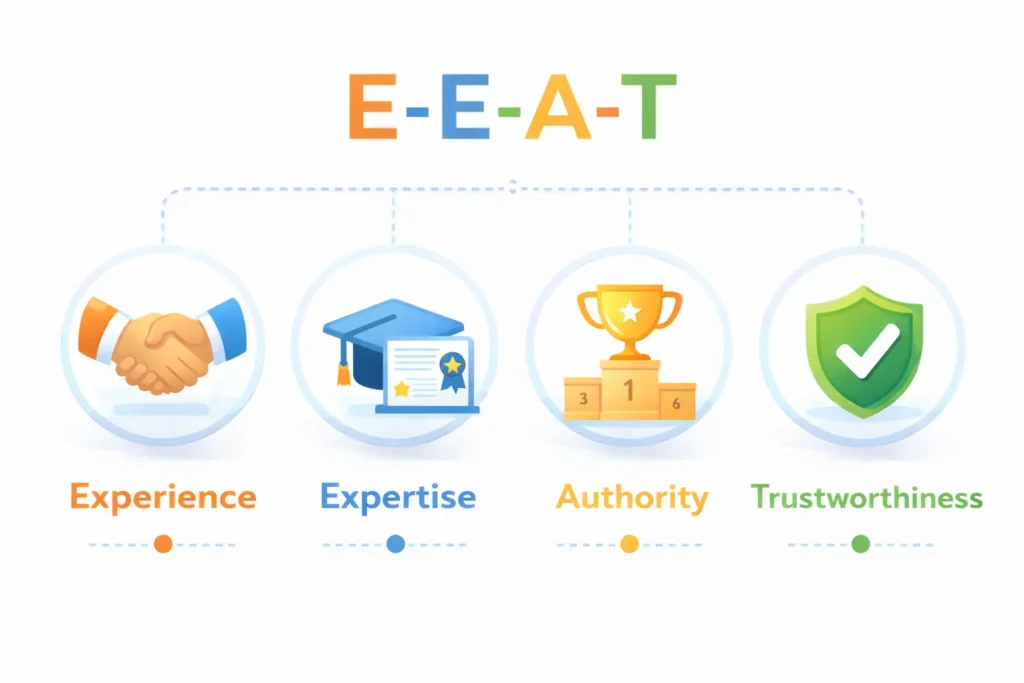
What is E-E-A-T and Why It Matters
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. While not a direct ranking factor in Google’s code, E-E-A-T represents the framework Google’s quality raters use to evaluate content. Sites that demonstrate strong E-E-A-T consistently outrank those that don’t.
The Problem: Many websites publish generic, AI-generated content without demonstrating real expertise or first-hand experience. This results in poor rankings, especially for topics that affect people’s health, finances, or safety (YMYL – Your Money Your Life content).
The Solution: Build genuine E-E-A-T signals throughout your website.
Experience: Demonstrate First-Hand Knowledge
Google added “Experience” to the original E-A-T framework in December 2022. This signals that first-hand experience with products, services, or topics significantly impacts rankings.
How to demonstrate experience:
- Share personal case studies with specific results and data
- Include before-and-after examples from your actual work
- Add author bios explaining relevant experience and credentials
- Use phrases like “In my 10 years of…” or “When I tested this…”
- Include original photos, screenshots, or videos from your experience
- Share specific challenges you faced and how you overcame them
Expertise: Prove Your Knowledge
Expertise means having deep knowledge in your field. Google looks for signals that content creators truly understand their subject matter.
How to demonstrate expertise:
- Author bylines on every article with credentials
- Detailed author pages listing qualifications, certifications, and publications
- Content depth that goes beyond surface-level information
- Technical accuracy and up-to-date information
- Citations from authoritative sources
- Industry-specific terminology used correctly
- Advanced insights that beginners couldn’t provide
Authoritativeness: Build Your Reputation
Authoritativeness is about your reputation in your industry. Are you recognized as a leader? Do other experts reference your work?
How to build authoritativeness:
- Earn backlinks from respected industry publications
- Get mentioned in news articles and industry reports
- Speak at conferences or host webinars
- Contribute guest posts to authoritative sites
- Build a strong social media presence in your niche
- Earn industry awards or certifications
- Get cited in research papers or industry reports
Trustworthiness: Establish Credibility
Trust is the most critical component. Google won’t rank content from sources users can’t trust, regardless of expertise level.
How to build trustworthiness:
- Install an SSL certificate (HTTPS) on your entire site
- Display clear contact information, including physical address
- Create detailed About Us and Privacy Policy pages
- Show genuine customer reviews and testimonials
- Maintain accurate, fact-checked information
- Update content regularly to keep it current
- Disclose affiliations, sponsorships, and conflicts of interest
- Respond professionally to customer reviews and feedback
- Display trust badges and security certifications
Search Intent: Matching Content to User Needs
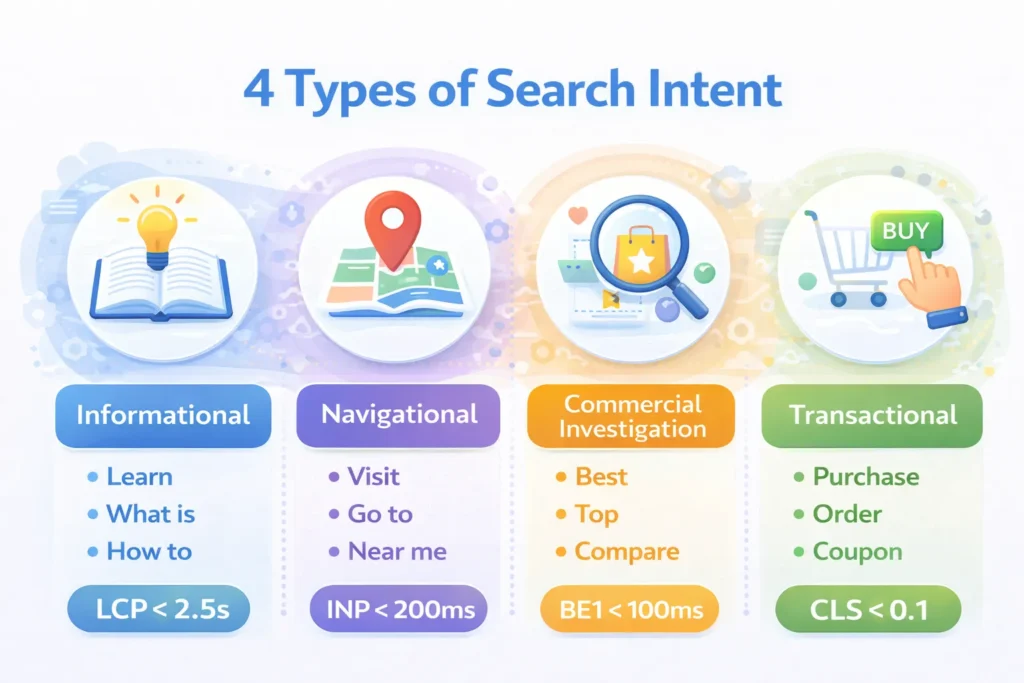
The Search Intent Problem
One of the biggest SEO mistakes is creating content around keywords without understanding why people search for them. If your content doesn’t match search intent, you won’t rank—even with perfect technical SEO.
The Four Types of Search Intent
1. Informational Intent: Users want to learn something or find information.
- Examples: “What are ranking factors?” “How does SEO work?”
- Content type: Guides, tutorials, explanations, definitions
- Optimization: Comprehensive coverage, clear explanations, examples
2. Navigational Intent Users want to find a specific website or page.
- Examples: “Facebook login,” “Amazon customer service.”
- Content type: Homepage, brand pages, login pages
- Optimization: Brand consistency, clear site structure
3. Commercial Investigation Intent Users are researching before making a purchase decision.
- Examples: “best SEO tools,” “WordPress vs Shopify Development.”
- Content type: Reviews, comparisons, “best of” lists
- Optimization: Honest comparisons, pros/cons, specific recommendations
4. Transactional Intent Users are ready to take action or make a purchase.
- Examples: “buy SEO software,” “hire SEO consultant.”
- Content type: Product pages, service pages, pricing pages
- Optimization: Clear CTAs, trust signals, pricing information
How to Align Content with Search Intent
Step 1: Analyze the SERP Search your target keyword and examine the first page results. What type of content ranks? Blog posts? Product pages? Videos? Match that format.
Step 2: Examine Content Depth. Are the top results 500 words or 3,000 words? Comprehensive or brief? Match the depth users expect.
Step 3: Check Content Angle. What angle do ranking pages take? Beginner guides? Advanced tutorials? Problem-solving? Match the expertise level and approach.
Step 4: Identify SERP Features. Do you see featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, or videos? Optimize your content to target these features.
Core Web Vitals: Technical Performance That Impacts Rankings
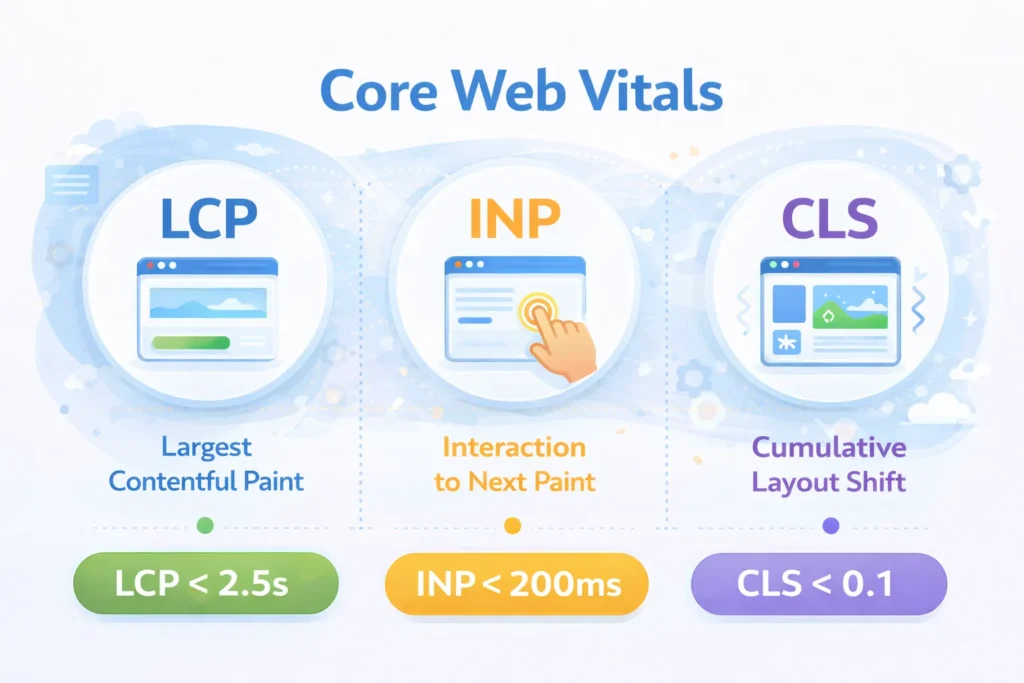
Why Core Web Vitals Matter
Core Web Vitals are Google’s official user experience metrics. Poor scores directly impact your rankings, especially when competing against sites with similar content quality.
The three critical metrics:
1. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – Loading Performance
LCP measures how long it takes for the main content to load on your page.
Target: Under 2.5 seconds. Common causes of poor LCP:
- Slow server response times
- Render-blocking JavaScript and CSS
- Large, unoptimized images
- Client-side rendering delays
How to fix LCP:
- Use a fast hosting provider with CDN
- Optimize and compress images (use WebP format)
- Implement lazy loading for below-the-fold content
- Remove unnecessary third-party scripts
- Preload critical resources
- Minimize CSS and JavaScript
- Use browser caching
2. Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – Responsiveness
INP replaced First Input Delay (FID) in March 2024. It measures how quickly your page responds to user interactions throughout the entire page visit.
Target: Under 200 milliseconds. Common causes of poor INP:
- Heavy JavaScript execution
- Long-running scripts
- Large DOM size
- Excessive third-party code
How to fix INP:
- Minimize JavaScript execution time
- Break up long tasks into smaller chunks
- Use web workers for heavy computations
- Optimize event handlers
- Reduce DOM complexity
- Remove unused JavaScript
- Defer non-critical scripts
3. Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – Visual Stability
CLS measures unexpected layout shifts that occur during page loading.
Target: Less than 0.1. Common causes of poor CLS:
- Images without dimensions
- Ads, embeds, or iframes without reserved space
- Dynamically injected content
- Web fonts causing FOIT/FOUT
How to fix CLS:
- Set width and height attributes on images and videos
- Reserve space for ads and embeds
- Avoid inserting content above existing content
- Use font-display: swap for web fonts
- Preload critical fonts
- Avoid animations that affect layout
Tools to Measure Core Web Vitals
- Google PageSpeed Insights: Detailed analysis with specific recommendations
- Google Search Console: Core Web Vitals report for your entire site
- Chrome DevTools: Real-time debugging during Website Development
- WebPageTest: Advanced performance analysis
Content Quality: Creating Ranking-Worthy Material
The Content Quality Problem
Publishing content isn’t enough. Google’s Helpful Content Update specifically targets thin, unhelpful content created primarily for search engines rather than users.
Elements of High-Quality Content
Comprehensive Coverage. Don’t just scratch the surface. Cover topics thoroughly with depth and detail. Answer all related questions a user might have. Include subtopics, examples, case studies, and practical applications.
Original Insights and Research: Regurgitating information available everywhere else won’t help you rank. Add unique value through:
- Original research and data
- Personal case studies
- Unique perspectives and analysis
- Expert interviews
- Proprietary methodologies
- Real-world testing and results
Content Freshness and Updates: Google favors fresh, updated content, especially for topics where information changes frequently.
How to maintain content freshness:
- Review and update content every 6-12 months
- Add new sections covering recent developments
- Update statistics, examples, and screenshots
- Add publication and “last updated” dates
- Remove outdated information
- Expand content based on new user questions
Readability and User Experience: Content must be easy to read and digest.
Best practices:
- Short paragraphs (2-4 sentences)
- Clear subheadings every 200-300 words
- Bullet points and numbered lists
- Bold important concepts
- Active voice instead of passive
- Simple language appropriate for your audience
- Proper grammar and spelling
Multimedia Integration Text-only content performs worse than content with multiple media types.
Include:
- Relevant images with descriptive alt text
- Explanatory videos
- Data visualizations and charts
- Screenshots for tutorials
- Infographics for complex information
Technical SEO Foundations
Website Architecture and Structure
Problem: Poor site structure confuses both users and search engines, leading to crawling issues and poor rankings.
Solution: Create a logical hierarchy
- Use a clear category structure
- Keep important pages within 3 clicks from the homepage
- Implement breadcrumb navigation
- Create an XML sitemap and submit to Google Search Console
- Use descriptive, keyword-rich URLs
- Implement proper header tag hierarchy (H1, H2, H3)
Mobile-First Optimization
Google uses mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of your site for ranking.
Essential mobile optimizations:
- Responsive design that adapts to all screen sizes
- Touch-friendly buttons (minimum 48×48 pixels)
- Readable text without zooming (16px minimum)
- Avoid horizontal scrolling
- Fast mobile loading speed
- No intrusive pop-ups on mobile
- Test with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool
HTTPS Security
HTTPS is a confirmed ranking factor. Sites without SSL certificates face ranking disadvantages.
Implementation:
- Install an SSL certificate on your entire site
- Redirect all HTTP URLs to HTTPS versions
- Update internal links to HTTPS
- Fix mixed content warnings
- Update sitemap with HTTPS URLs
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Structured data helps Google understand your content and can earn you rich snippets in search results.
Most valuable schema types:
- Article Schema: For blog posts and news articles
- FAQ Schema: To appear in People Also Ask boxes
- Product Schema: For e-commerce pages (enables review stars, pricing)
- Local Business Schema: For local SEO (address, hours, reviews)
- How-To Schema: For instructional content
- Breadcrumb Schema: For navigation clarity
Implementation: Use JSON-LD format (Google’s preferred method) and test with Google’s Rich Results Test tool.
On-Page SEO Optimization

Title Tag Optimization
Your title tag is one of the most important on-page factors.
Best practices:
- Include the primary keyword near the beginning
- Keep under 60 characters to avoid truncation
- Make it compelling to improve the click-through rate
- Include your brand name at the end
- Make each title unique
- Match search intent
Example: Good: “Google Ranking Factors 2026: Complete SEO Guide | YourBrand” Bad: “Ranking Factors | SEO Optimization| Google | Guide | YourBrand”
Meta Description Optimization
While not a direct ranking factor, meta descriptions impact click-through rate, which influences rankings.
Best practices:
- Include the primary keyword naturally
- Keep 150-160 characters
- Include a clear call-to-action
- Accurately describe page content
- Make it compelling and benefit-focused
Header Tag Structure
Headers organize content and help Google understand your page structure.
Best practices:
- One H1 per page (typically your title)
- Use H2s for main sections
- Use H3s for subsections under H2s
- Include keywords naturally in headers
- Make headers descriptive and useful
- Maintain logical hierarchy
URL Structure
Clean, descriptive URLs perform better than complex ones.
Best practices:
- Keep URLs short and readable
- Include the target keyword
- Use hyphens to separate words
- Avoid numbers, dates, and special characters
- Use lowercase letters
- Match URL to content topic
Example: Good: yoursite.com/google-ranking-factors Bad: yoursite.com/p?id=12345&cat=seo&post=rank
Image Optimization
Optimized images improve page speed and can rank in image search.
Best practices:
- Use descriptive file names with keywords
- Add descriptive alt text to every image
- Compress images to reduce file size
- Use next-gen formats (WebP)
- Set width and height attributes
- Use lazy loading for below-the-fold images
- Create an image sitemap for important images
Internal Linking Strategy
Internal links distribute authority throughout your site and help Google discover content.
Best practices:
- Link to related content within articles
- Use descriptive anchor text (not “click here”)
- Link to important pages more frequently
- Create hub pages that link to related content
- Ensure all pages are accessible within 3-clicks
- Fix broken internal links regularly
- Link from high-authority pages to new content
Backlinks and Off-Page Authority
Why Backlinks Still Matter
Backlinks remain one of Google’s strongest ranking signals. Quality links from authoritative sites tell Google your content is valuable and trustworthy.
Quality Over Quantity
High-quality backlink characteristics:
- From websites with high domain authority
- From relevant, topically related sites
- From pages with high authority themselves
- Editorial links (not paid or exchanged)
- Natural anchor text
- From content contextually related to yours
- DoFollow links (though NoFollow has value too)
Natural Link Building Strategies
1. Create Linkable Assets. Develop content so valuable that people naturally want to link to it:
- Original research and data
- Comprehensive guides
- Industry surveys and statistics
- Free tools and calculators
- Unique case studies
- Expert roundups
2. Digital PR and Outreach
- Share newsworthy content with journalists
- Respond to journalist requests on HARO
- Create data-driven stories for publications
- Partner with influencers in your niche
3. Guest Posting: Write valuable content for authoritative sites in your industry. Focus on editorial relationships, not just links.
4. Broken Link Building: Find broken links on relevant websites and suggest your content as a replacement.
5. Competitor Backlink Analysis Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to see where competitors get links, then pursue similar opportunities.
Avoiding Toxic Links
Never:
- Buy backlinks from link farms
- Participate in link exchange schemes
- Use automated link-building tools
- Get links from spammy directories
- Create fake blog networks
These tactics will get you penalized. Focus on earning legitimate editorial links.
Local SEO Ranking Factors

Google Business Profile Optimization
For local businesses, your Google Business Profile is critical.
Complete optimization:
- Verify your business
- Choose the most specific category
- Add complete business information (hours, phone, website)
- Write a keyword-rich business description
- Upload high-quality photos regularly
- Post updates weekly
- Respond to all reviews quickly
- Add products/services with descriptions
- Use Google Posts for updates and offers
Local Citations and NAP Consistency
NAP (Name, Address, Phone) consistency across the web builds trust.
Action steps:
- List your business in major directories (Yelp, Yellow Pages, industry-specific)
- Ensure exact NAP consistency everywhere
- Keep information updated across all platforms
- Remove duplicate listings
- Build citations on relevant local sites
Reviews and Reputation Management
Reviews significantly impact local rankings.
Strategy:
- Ask satisfied customers for reviews
- Make it easy with direct review links
- Respond to all reviews (positive and negative)
- Address negative reviews professionally
- Generate consistent review velocity
- Reviews on Google matter most, but reviews on other platforms help the overall reputation
Local Content and Keywords
Create content targeting local search terms.
Examples:
- Location-specific service pages
- Local area guides
- Community involvement posts
- Local event coverage
- City/neighborhood-specific blog content
AI and Search Generative Experience (SGE)
How AI Overviews Impact Rankings
Google’s AI Overviews (formerly SGE) now appear for many searches, providing AI-generated answers at the top of results. While this reduces organic clicks for some queries, being cited in AI Overviews is valuable.
Optimizing for AI-Generated Answers
Best practices:
- Create clear, direct answers to common questions
- Use the FAQ sections
- Structure content with clear headers
- Implement FAQ schema markup
- Provide concise definitions and explanations
- Include data and statistics
- Cite authoritative sources
- Write in a natural, conversational tone
- Answer questions completely and accurately
Voice Search Optimization
With AI assistants growing, voice search optimization matters more than ever.
Optimization strategies:
- Target conversational, long-tail keywords
- Answer questions directly
- Use natural language in content
- Focus on featured snippet optimization
- Include local information for local businesses
- Create FAQ pages
- Optimize for “near me” searches
User Behavior Signals
How User Engagement Affects Rankings
Google monitors how users interact with search results. Positive engagement signals suggest your content satisfies search intent.
Critical User Signals
Click-Through Rate (CTR) A higher CTR from search results signals relevance. Improve with:
- Compelling titles
- Descriptive meta descriptions
- Rich snippets (review stars, FAQs)
- Relevant URLs
Dwell Time: Time spent on your page before returning to search results. Improve with:
- Engaging introduction that hooks readers
- Well-formatted, easy-to-read content
- Internal links to related content
- Multimedia elements
- Fast page loading
Bounce Rate: Percentage of visitors leaving immediately. Reduce by:
- Matching content to search intent
- Fast loading speed
- Mobile optimization
- Clear navigation
- Relevant, valuable content
Return Visits: Users returning to your site signal value. Encourage with:
- Genuinely helpful content
- Regular updates
- Email newsletter
- Bookmark-worthy resources
Common SEO Mistakes That Hurt Rankings
Keyword Stuffing
Overusing keywords makes content unreadable and triggers penalties. Use keywords naturally and focus on topic coverage instead.
Thin Content
Pages with little value or duplicate content won’t rank. Every page should provide substantial, unique value.
Ignoring Mobile Users
With mobile-first indexing, a poor mobile experience kills rankings. Test thoroughly on actual devices.
Slow Page Speed
Users and Google hate slow sites. Prioritize performance optimization.
Toxic Backlinks
Low-quality or spammy backlinks harm your profile. Monitor and disavow when necessary.
Poor User Experience
Intrusive pop-ups, confusing navigation, and hard-to-read content increase bounce rates and hurt rankings.
Neglecting Technical SEO
Broken links, redirect chains, crawl errors, and indexing issues prevent Google from properly evaluating your site.
Action Plan: Prioritizing Ranking Factors
You can’t optimize everything at once. Here’s your priority order:
Phase 1: Foundation (Month 1)
- Fix technical SEO issues (crawlability, mobile, HTTPS)
- Improve Core Web Vitals
- Optimize on-page elements (titles, headers, URLs)
- Ensure content matches search intent
Phase 2: Content Quality (Months 2-3) 5. Build E-E-A-T signals (author bios, credentials, about page) 6. Expand thin content to comprehensive guides 7. Add structured data markup 8. Optimize for featured snippets
Phase 3: Authority Building (Months 4-6) 9. Create linkable assets 10. Begin outreach for quality backlinks 11. Build local citations (if applicable) 12. Generate and respond to reviews
Phase 4: Optimization (Ongoing) 13. Monitor user behavior metrics 14. Update content regularly 15. Analyze competitor strategies 16. Test and refine approaches
Conclusion
Google ranking factors will continue evolving, but the core principles remain consistent: create exceptional content that genuinely helps users, ensure your website provides an excellent technical experience, and build legitimate authority in your niche.
Stop chasing algorithm updates and quick fixes. Instead, focus on the fundamentals outlined in this guide. Prioritize user experience over search engine manipulation. Demonstrate real expertise and trustworthiness. Build quality over quantity in both content and backlinks.
The websites that rank consistently are those that deserve to rank—they provide the most value, best experience, and strongest expertise in their field. Make that your goal, and rankings will follow.
Start with your foundation: fix technical issues, optimize Core Web Vitals, and ensure your content matches search intent. Then build authority through quality content and legitimate link building. Monitor your progress, learn from results, and continuously improve.
SEO success in 2026 requires patience, consistency, and genuine commitment to quality. Follow this guide, avoid shortcuts, and you’ll build sustainable rankings that drive real business results.
Faqs
Google uses over 200 ranking factors, though not all carry equal weight. Focus on the major factors outlined in this guide rather than trying to optimize for everything.
No single factor guarantees rankings. However, high-quality, relevant content that matches search intent and demonstrates E-E-A-T is foundational. Without good content, other optimizations won’t help.
Typically 3-6 months for competitive keywords, though you might see improvements for less competitive terms sooner. SEO is a long-term strategy requiring consistent effort.
Not directly, but social media can drive traffic, increase brand awareness, and lead to backlinks—all of which indirectly benefit SEO.
Review important pages every 6-12 months. Update whenever information becomes outdated, new developments occur in your industry, or you can add significant new value.
Yes, quality backlinks remain a critical ranking factor. Focus on earning editorial links from authoritative, relevant sites.
AI can assist with research and drafting, but Google emphasizes that content should demonstrate genuine experience and expertise.

