If your website isn’t ranking despite publishing content regularly, you’re facing one of the most common digital marketing challenges today. The problem isn’t your effort—it’s your approach. Google’s algorithm has evolved beyond simple keyword matching, and outdated SEO tactics from 2015 no longer work.
In 2026, a successful SEO strategy requires understanding search intent, building topical authority, optimizing for AI-powered search engines, and establishing trust through E-E-A-T signals. This comprehensive guide solves the core problems preventing your website from ranking and provides actionable solutions you can implement immediately.
1. Understanding Modern SEO Strategy
SEO strategy is no longer about stuffing keywords into content and building random backlinks. Modern search engine optimization is a systematic approach to making your website the most authoritative, trustworthy, and relevant source for specific topics.
The core principle: Google wants to deliver the best answer to user queries. Your job is to prove your website deserves that position.
What Makes a Good SEO Strategy in 2026?
A successful SEO strategy addresses three critical dimensions:
Technical Foundation: Your website must be crawlable, fast, mobile-friendly, and technically sound. Without this foundation, even the best content won’t rank.
Content Authority: You must demonstrate comprehensive expertise in your niche through interconnected, high-quality content that covers topics thoroughly, not just individual keywords.
Trust Signals: Google evaluates your credibility through backlinks, author expertise, content accuracy, and user engagement metrics.
2. The Core Problem: Why Most Websites Don’t Rank
Before diving into solutions, let’s identify the specific problems preventing your website from ranking:
Problem 1: Targeting Keywords Without Understanding Intent
You optimize for “best CRM software,” but Google shows comparison reviews, while your page is a product landing page. The intent mismatch kills your rankings.
Solution: Map content to the four types of search intent—informational, navigational, commercial, and transactional. Create specific content for each intent type.
Problem 2: Thin Content Coverage
You publish one article about “email marketing” and expect to rank against competitors with 50 interconnected articles covering every subtopic.
Solution: Build content clusters around core topics, demonstrating comprehensive expertise that Google recognizes as topical authority.
Problem 3: Technical Issues Blocking Crawlers
Broken site architecture, slow page speed, mobile issues, or crawlability problems prevent Google from properly indexing your content.
Solution: Conduct regular technical SEO audits using Google Search Console and fix Core Web Vitals, crawl errors, and mobile usability issues.
Problem 4: Lack of Trust Signals
Your content has no author credentials, no backlinks from authoritative sites, and no expertise indicators that satisfy Google’s E-E-A-T requirements.
Solution: Add author bios with credentials, earn topically relevant backlinks, include original research and data, and update content regularly.
Problem 5: Ignoring AI-Powered Search
You optimize only for traditional Google search while ignoring AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other generative search engines gaining market share.
Solution: Implement Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) strategies to ensure your content gets cited in AI-generated answers.
3. Search Intent: The Foundation of Modern SEO
Search intent is the reason behind a user’s query. Google has become exceptionally good at understanding what users really want, and ranks content that matches that intent.
The Four Types of Search Intent
Informational Intent: Users want to learn something.
- Examples: “What is SEO?” “How does Google ranking work?” “SEO strategy guide”
- Content type: Comprehensive guides, tutorials, how-to articles, explainer content
- User goal: Education and understanding
Navigational Intent: Users want to find a specific website or page.
- Examples: “Google Search Console login,” “SEMrush pricing,” “Ahrefs keyword explorer”
- Content type: Brand pages, product pages, login portals
- User goal: Reaching a known destination
Commercial Intent: Users are researching before making a decision.
- Examples: “best SEO tools 2026,” “Ahrefs vs SEMrush,” “SEO agency reviews”
- Content type: Comparison articles, reviews, best-of lists, case studies
- User goal: Evaluation and comparison
Transactional Intent: Users are ready to take action.
- Examples: “buy SEO Strategy audit,” “hire SEO consultant,” “SEO services pricing.”
- Content type: Service pages, product pages, pricing pages, signup forms
- User goal: Conversion and purchase
How to Identify Search Intent
Step 1: Analyze SERP results. Search your target keyword and examine the top 10 results. What format dominates? If all top results are listicles, Google interprets that keyword as commercial intent.
2: Check People Also Ask. The questions reveal what users actually want to know about the topic.
3: Examine query modifiers. Words like “how to,” “best,” “vs,” “buy,” and “near me” signal specific intent types.
4: Match content format to intent. Don’t write a product sales page for an informational query or a tutorial for a transactional query.
Intent-Based Content Strategy
Create content for each stage of the user journey:
- Awareness stage (Informational): Educational content that attracts users discovering the problem
- Consideration stage (Commercial): Comparison content helping users evaluate solutions
- Decision stage (Transactional): Conversion-optimized content for ready-to-buy users
This strategy ensures you capture users at every funnel stage, building traffic and conversions simultaneously.
4. Building Topical Authority Through Content Clusters
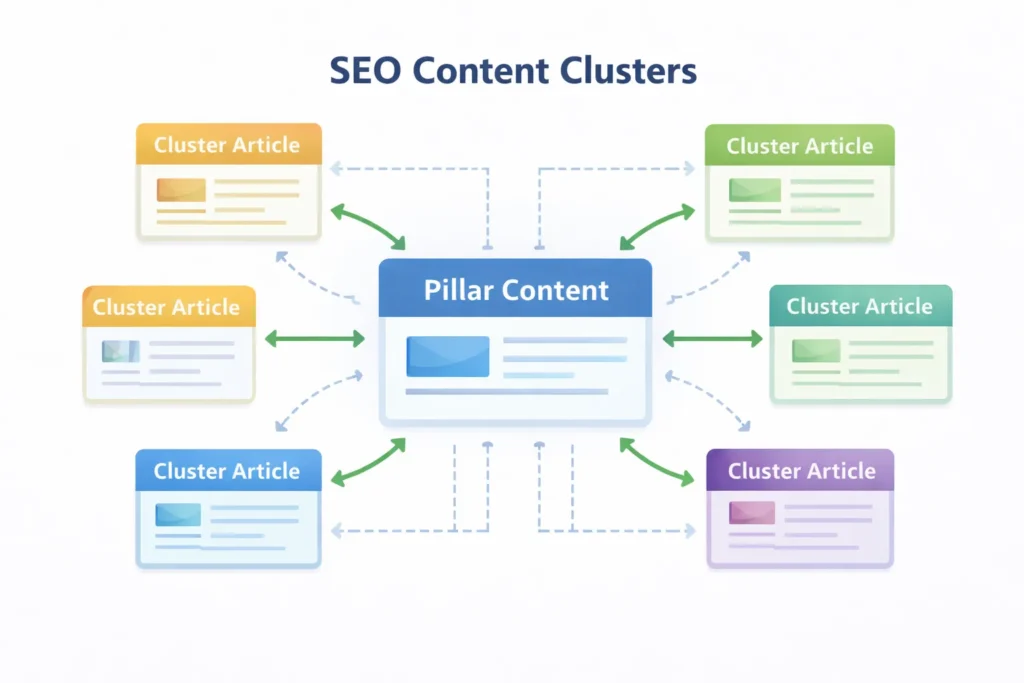
Topical authority is Google’s measure of how comprehensively your website covers a specific subject. This is the single most important ranking factor for 2026.
Why Topical Authority Matters
Publishing one article about “project management” and expecting to rank against competitors with 50 interconnected articles is like showing up to a university lecture after reading one chapter while your competitor wrote the textbook.
Google doesn’t just want good content—it wants proof you’re a genuine expert on the topic. Comprehensive coverage across interconnected articles demonstrates that expertise.
The Content Cluster Model
A content cluster consists of:
Pillar Content: One comprehensive guide (3,000-6,000 words) that broadly covers the main topic. Example: “Complete Guide to Project Management”
Cluster Content: 10-20 detailed articles (1,500-2,500 words) covering specific subtopics. Examples: “Agile vs Waterfall Methodology,” “Project Management Software Comparison,” “Project Risk Management Strategies”
Supporting Content: 30-50 focused articles (800-1,500 words) addressing specific questions and long-tail queries. Examples: “How to create a Gantt chart in Excel,” “What is project scope creep?”
How to Build Content Clusters
Step 1: Choose a narrow topic. Instead of “Digital Marketing,” choose “B2B SaaS content marketing for early-stage startups.” Narrow topics are easier to dominate.
2: Map the topic landscape. Use keyword research tools, Google’s People Also Ask, competitor analysis, and customer questions to identify 50-100 subtopics.
3: Create your pillar content. Write the comprehensive guide first—this becomes your hub that everything links to.
4: Build cluster content systematically. Publish 4-6 articles monthly, ensuring each links to the pillar and to related cluster articles.
5: Implement strategic internal linking. Every cluster article links back to the pillar—the pillar links to all clusters. Clusters link to related clusters. This web of connections shows Google’s comprehensive coverage.
Internal Linking Strategy
Hub-and-spoke model:
- Pillar content is the hub
- Cluster articles are spokes
- All spokes connect to the hub
- Spokes connect to related spokes
Best practices:
- Use descriptive anchor text (not “click here”)
- Link from relevant context
- Ensure no article is more than 3 clicks from the homepage
- Update old articles with links to new content
- Implement breadcrumb navigation
5. E-E-A-T: Establishing Trust and Expertise
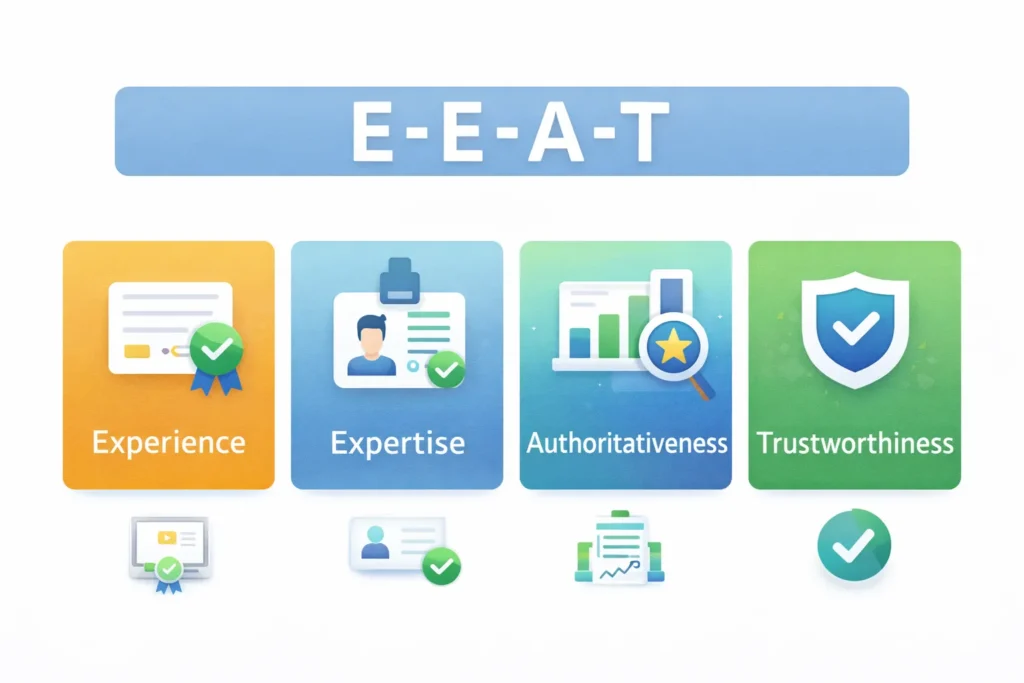
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. These are the quality signals Google uses to evaluate content credibility, especially for topics affecting health, finance, safety, and major life decisions.
Experience: Demonstrating First-Hand Knowledge
Problem: Generic content written by someone who has never actually used the product or service they’re reviewing.
Solution:
- Include specific details that only someone with real experience would know
- Add case studies with actual results and data
- Use screenshots, videos, or photos showing hands-on experience
- Share original insights, not just rehashed information from other sources
- Mention specific challenges encountered and how you solved them
Expertise: Proving You Know the Subject
Problem: Content written by generalists without deep subject knowledge.
Solution:
- Add author bios with relevant credentials, certifications, and experience
- Include specific technical details that demonstrate depth
- Reference industry standards, methodologies, and frameworks correctly
- Cite authoritative sources and research
- Use proper terminology and explain complex concepts accurately
Authoritativeness: Building Recognition in Your Field
Problem: Your website and authors are unknown in your industry.
Solution:
- Earn backlinks from recognized authorities in your niche
- Get author bylines on reputable industry publications
- Speak at conferences or industry events
- Participate in industry forums and communities
- Build social proof through testimonials and case studies
- Achieve industry certifications or awards
Trustworthiness: Establishing Credibility
Problem: Users and Google can’t verify your information or credentials.
Solution:
- Display clear contact information and physical address
- Implement HTTPS security across the entire site
- Show privacy policy and terms of service
- Display clear authorship on every article
- Fact-check all claims and include citations
- Update content regularly to maintain accuracy
- Respond to user comments and questions
- Display trust badges, certifications, and professional affiliations
How to Implement E-E-A-T
For every piece of content:
- Add a detailed author bio with credentials and photo
- Include the publication and last updated date
- Cite authoritative sources for claims and statistics
- Add original insights from real experience
- Use schema markup to highlight author expertise
- Link to related content demonstrating comprehensive coverage
6. Technical SEO: Fixing Ranking Blockers
Technical SEO Strategy issues are invisible to users but devastating to rankings. If Google can’t properly crawl, index, and understand your site, your content won’t rank regardless of quality.
Problem 1: Poor Site Architecture
Symptoms: Pages buried deep in the site structure, inconsistent navigation, orphan pages with no internal links.
Solution:
- Implement clear hierarchy: Homepage → Category → Subcategory → Article
- Ensure important pages are within 3 clicks of the homepage
- Create logical URL structure: example.com/category/subcategory/article-name
- Build an HTML sitemap for users and an XML sitemap for search engines
- Use breadcrumb navigation on every page
Problem 2: Crawlability Issues
Symptoms: Pages not appearing in Google index, crawl errors in Search Console, blocked resources.
Solution:
- Check and optimize the robots.txt file
- Remove blocks on important pages
- Fix broken internal links
- Ensure proper use of noindex tags (not accidentally blocking important pages)
- Submit XML sitemap to Google Search Console
- Monitor crawl stats and fix errors weekly
Problem 3: Slow Page Speed
Symptoms: High bounce rates, poor Core Web Vitals scores, and user complaints about loading times.
Solution:
- Compress images (use WebP format, max 100KB per image)
- Minimize CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files
- Enable browser caching
- Use Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Implement lazy loading for images below the fold
- Remove unnecessary plugins and scripts
- Choose fast hosting with a good server response time
Problem 4: Core Web Vitals Failures
Google’s page experience signals measure loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. Should be under 2.5 seconds.
Solution:
- Optimize server response time
- Remove render-blocking resources
- Optimize and compress images
- Implement resource preloading
Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Measures responsiveness. Should be under 200 milliseconds.
Solution:
- Minimize JavaScript execution time
- Break up long tasks
- Optimize event handlers
- Use web workers for heavy computations
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. Should be under 0.1.
Solution:
- Set size attributes for images and videos
- Reserve space for ads and embeds
- Avoid inserting content above existing content
- Use transform animations instead of property animations
Problem 5: Mobile Usability Issues
Symptoms: Google Search Console shows mobile usability errors and high mobile bounce rates.
Solution:
- Implement responsive design
- Ensure text is readable without zooming (minimum 16px font)
- Make buttons and links large enough to tap (minimum 48×48 pixels)
- Avoid horizontal scrolling
- Test on real mobile devices, not just emulators
- Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool
Problem 6: Missing or Incorrect Schema Markup
Symptoms: Your content doesn’t show rich snippets in search results, missing star ratings, and no FAQ accordion in SERPs.
Solution:
- Implement schema markup for your content type:
- Article schema for blog posts
- FAQ schema for question-answer content
- How-to schema for tutorials
- Product schema for e-commerce
- Local Business schema for location-based businesses
- Review schema for ratings and testimonials
- Use JSON-LD format (Google’s preference)
- Test with Google’s Rich Results Test tool
- Monitor rich result performance in Search Console
7. On-Page SEO Optimization
On-page SEO involves optimizing individual pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic. This is where you prove to Google that your page is the best result for a specific query.
Title Tag Optimization
Problem: Generic titles that don’t match search intent or include no compelling reason to click.
Solution:
- Include the primary keyword near the beginning
- Keep under 60 characters to avoid truncation
- Make it compelling and click-worthy
- Match the search intent
- Include the year for freshness when relevant
- Example: “SEO Strategy 2026: 15 Proven Techniques to Rank #1 on Google”
Meta Description Optimization
Problem: Missing meta descriptions or generic auto-generated snippets that don’t entice clicks.
Solution:
- Include primary and secondary keywords naturally
- Keep between 150-160 characters
- Include a clear benefit or promise
- Add a call-to-action
- Make it unique for every page
- Example: “Struggling with rankings? Learn 15 proven SEO strategies that helped 200+ businesses reach page 1. Includes checklist and templates.”
Header Tag Hierarchy
Problem: Missing H1 tags, multiple H1s, or skipping heading levels (H1 to H3 without H2).
Solution:
- One H1 per page containing the primary keyword
- Use H2s for main sections
- Use H3s for subsections under H2s
- Include keywords naturally in headers
- Make headers descriptive and scannable
- Structure creates a logical content outline
Content Optimization
Problem: Thin content, keyword stuffing, or content that doesn’t comprehensively answer the query.
Solution:
- Write comprehensive content (minimum 1,500 words for competitive topics)
- Cover the topic thoroughly, addressing related questions
- Use primary keyword naturally 3-5 times per 1,000 words
- Include semantic keywords and related entities
- Break content into scannable sections with clear headers
- Add bullet points and numbered lists for readability
- Include examples, case studies, and actionable advice
- Answer related questions users might have
- Update regularly with fresh information
Image Optimization
Problem: Huge image files are slowing page speed, missing alt text, reducing accessibility and SEO value.
Solution:
- Compress images to under 100KB without quality loss
- Use descriptive file names (seo-strategy-diagram.jpg, not IMG_1234.jpg)
- Write descriptive alt text including relevant keywords
- Use WebP format for better compression
- Implement lazy loading for below-fold images
- Include relevant images to break up text and increase engagement
- Add image schema markup when appropriate
Internal Linking
Problem: Orphan pages with no internal links, excessive links creating “link soup,” or irrelevant link suggestions.
Solution:
- Link to 3-5 relevant internal pages in every article
- Use descriptive anchor text
- Link to both related content and conversion pages
- Implement contextual linking (links within content flow)
- Create topic-based linking patterns (content clusters)
- Avoid excessive footer or sidebar links
URL Structure
Problem: Long, parameter-filled URLs that are neither user-friendly nor SEO-friendly.
Solution:
- Keep URLs short and descriptive
- Include primary keyword
- Use hyphens to separate words (not underscores)
- Avoid parameters and session IDs when possible
- Create a logical hierarchy in the URL path
- Example: gooddomain.com/seo/strategy-guide (not gooddomain.com/p?id=12345)
8. Off-Page SEO and Link Building Strategy
Off-page SEO Strategy refers to actions taken outside your website to impact rankings, primarily through earning high-quality backlinks that signal authority and trust.
Understanding Backlink Quality
Problem: Focusing on backlink quantity instead of quality, resulting in spammy links that hurt rather than help.
What makes a quality backlink:
- Relevance: Link comes from a site in your industry or a related topic area
- Authority: Linking site has high domain authority and topical authority
- Placement: Link is in the main content, not the footer or sidebar
- Context: Link is surrounded by relevant content
- Anchor text: Natural, varied anchor text (not always exact-match keywords)
- DoFollow status: Link passes PageRank (though some NoFollow links are natural)
Link Building Strategies That Work
Strategy 1: Create Linkable Assets
Problem: Your content is good, but not remarkable enough for others to naturally link to.
Solution: Create resources that provide unique value:
- Original research and industry surveys
- Comprehensive guides (10,000+ words pillar content)
- Free tools and calculators
- Industry statistics and data visualization
- Templates and downloadable resources
- Unique case studies with real data
Strategy 2: Digital PR and Content Promotion
Problem: Publishing great content, but nobody knows it exists.
Solution:
- Identify journalists and bloggers covering your topic
- Send personalized outreach when you publish linkable assets
- Offer unique data or expert quotes for their articles
- Respond to journalist requests on platforms like HARO and Qwoted
- Create newsworthy content tied to trends or current events
Strategy 3: Guest Posting on Relevant Sites
Problem: Mass guest posting on irrelevant, low-quality sites.
Solution:
- Target sites with genuine topical relevance
- Focus on quality over quantity (5 guest posts on authoritative sites beat 50 on low-quality blogs)
- Provide genuinely valuable content, not thin promotional pieces
- Build relationships with editors before pitching
- Include natural contextual links, not forced keyword anchors
Strategy 4: Broken Link Building
Problem: Competitors have backlinks you don’t, but they’re hard to earn.
Solution:
- Find broken links on authoritative sites in your niche using tools like Ahrefs
- Check if you have content that could replace the broken resource
- Contact site owner with a helpful heads-up about the broken link
- Suggest your relevant content as a replacement
- Emphasize the value you’re providing (fixing their user experience)
Strategy 5: Competitor Backlink Analysis
Problem: Not knowing where your competitors are getting their authority.
Solution:
- Use Ahrefs or SEMrush to analyze competitor backlink profiles
- Identify their highest-authority backlinks
- Assess which of those opportunities you can realistically pursue
- Create better content than what’s currently linked
- Reach out to the same sources with improved resources
Link Building Mistakes to Avoid
Purchasing links is risky: Google may penalize sites that buy backlinks, potentially deindexing your pages.
Steer clear of link farms and PBNs: Temporary gains from private blog networks can lead to severe penalties.
Use varied anchor text: Excessive exact-match anchors look manipulative and hurt SEO Strategy.
Ensure links are relevant: Backlinks from unrelated sites, like a gambling website linking to an SEO blog, raise red flags.
Limit reciprocal linking schemes: Overusing “you link to me, I link to you” patterns can appear manipulative to Google.
9. AI Search Optimization (GEO)

Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of optimizing content for AI-powered search engines like Google AI Overviews, ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and other generative AI systems that provide direct answers instead of link lists.
Why GEO Matters in 2026
The problem: You rank #1 in traditional Google search, but your content never gets cited in AI-generated answers, causing you to miss 40%+ of search traffic now flowing through AI systems.
The shift: Users increasingly ask AI assistants questions instead of searching Google. If AI systems don’t reference your content, you become invisible to a massive and growing audience.
How AI Search Differs from Traditional Search
Traditional SEO: Google shows 10 blue links; users click through to websites.
GEO: AI systems synthesize information from multiple sources and present a direct answer; users may never visit your site, but you gain brand visibility through citations.
Key differences:
- Format: Long-form answers vs link lists
- Sources: Multiple sources cited in one answer
- User behavior: Users read the AI answer rather than clicking links
- Value: Being cited builds authority even without traffic
- Competition: You compete for citation inclusion, not position #1
Strategies to Optimize for AI Search
Strategy 1: Provide Clear, Direct Answers
Problem: Your content buries the answer in paragraphs of fluff.
Solution:
- Start articles with a concise answer to the main question
- Use clear formatting: questions as headers, answers immediately following
- Create FAQ sections with direct question-answer pairs
- Use structured data (FAQ schema) to help AI extract information
Strategy 2: Build Comprehensive Topical Authority
Problem: AI systems prefer citing recognized authorities with comprehensive coverage.
Solution:
- Build content clusters demonstrating deep expertise
- Cover topics from multiple angles and depths
- Interlink related content extensively
- Update content regularly to maintain authority
Strategy 3: Use Structured Data Extensively
Problem: AI systems struggle to understand unstructured content.
Solution:
- Implement schema markup for all content types
- Use Article, FAQ, How-to, and other relevant schemas
- Structure data in clear hierarchies
- Test schema implementation with validation tools
Strategy 4: Optimize for Citation Inclusion
Problem: Your facts are correct, but not formatted for easy citation.
Solution:
- Present statistics and facts clearly with attribution
- Use clear attribution (cite your sources, so AI can cite you)
- Include unique data and original research
- Format information in easily extractable formats (lists, tables, definitions)
- Use quotable statements and key takeaways
Strategy 5: Focus on Authoritative Content Signals
Problem: AI systems prioritize trusted, authoritative sources.
Solution:
- Display clear author credentials and expertise
- Include publication and update dates
- Cite reputable sources throughout the content
- Build backlinks from recognized authorities
- Maintain content accuracy and factual correctness
Zero-Click Search Strategy
Problem: AI provides the answer; users never visit your site, so you get visibility but no traffic.
Solution:
- View citations as branding opportunities, not just traffic drivers
- Include brand name prominently in cited content
- Use citations to build authority that drives direct searches
- Create content that naturally requires clicking through (tools, detailed guides, downloadable resources)
- Balance citation-optimized content with conversion-focused content
10. Semantic SEO and Entity Optimization
Semantic SEO Strategy focuses on meaning and context rather than just keywords. Google uses entity-based understanding to connect concepts, evaluate expertise, and determine the most relevant results.
What Are Entities?
Entities are distinct, unique things that Google recognizes in its Knowledge Graph: people, places, concepts, brands, events, or objects.
Examples:
- People: Neil Patel, Rand Fishkin
- Companies: Google, Ahrefs, SEMrush
- Concepts: Search engine optimization, topical authority, backlinks
- Places: Silicon Valley, Mountain View
- Methodologies: Agile, Scrum, Waterfall
How Google Uses Entities
Google connects entities through relationships in its Knowledge Graph:
- “Neil Patel” → “SEO expert” → “digital marketing”
- “Ahrefs” → “SEO tool” → “backlink analysis”
- “Content clusters” → “topical authority” → “SEO strategy”
When your content demonstrates understanding of these entity relationships, Google recognizes your topical expertise.
Semantic SEO Implementation
Strategy 1: Entity Optimization
Problem: Your content mentions topics but doesn’t demonstrate understanding of entity relationships.
Solution:
- Identify core entities related to your topic
- Mention related entities naturally throughout content
- Explain relationships between entities
- Link entities to authoritative sources
- Use proper names and terminology consistently
Example: For an article about “SEO tools,” mention specific tools (Ahrefs, SEMrush, Moz), their features (backlink analysis, keyword research, rank tracking), related concepts (domain authority, search volume, SERP analysis), and recognized experts (Rand Fishkin, Brian Dean).
Strategy 2: Topic Modeling
Problem: You optimize for one keyword but miss semantically related terms and concepts.
Solution:
- Use tools like Clearscope or Surfer SEO Strategy to identify semantically related terms
- Analyze top-ranking content for related concepts they cover
- Include LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing) keywords naturally
- Cover subtopics comprehensively, not just the main keyword
Strategy 3: Question-Based Content
Problem: Your content doesn’t address the full spectrum of user questions around your topic.
Solution:
- Research “People Also Ask” boxes for your keywords
- Use AnswerThePublic to find question variations
- Create FAQ sections answering related questions
- Structure content to address various question types (what, why, how, when, who, where)
Strategy 4: Natural Language Optimization
Problem: Content reads like it was written for robots, not humans.
Solution:
- Write conversationally, matching how people actually speak
- Use varied vocabulary (synonyms and related terms)
- Avoid keyword stuffing and unnatural phrasing
- Structure content logically, as humans process information
- Use transition words and phrases for readability
11. Local SEO Strategy
Local SEO Strategy optimizes your online presence to attract customers from local searches. Critical for businesses serving specific geographic areas.
Google Business Profile Optimization
Problem: An incomplete or unoptimized Google Business Profile is causing poor local visibility.
Solution:
- Claim and verify your Google Business Profile
- Complete every section: business name, address, phone, hours, services, description
- Choose accurate business categories (primary and secondary)
- Add high-quality photos (exterior, interior, products, team)
- Collect and respond to customer reviews regularly
- Post updates, offers, and events weekly
- Verify business information is consistent across all platforms
Local Citations and NAP Consistency
Problem: Inconsistent business information across web directories is causing trust issues.
NAP = Name, Address, Phone Number
Solution:
- Ensure identical NAP information across all platforms
- List business in relevant directories: Google Business Profile, Bing Places, Yelp, industry-specific directories
- Fix inconsistencies (different phone formats, abbreviated vs full street names)
- Remove duplicate listings
- Build citations on authoritative local and industry directories
Local Content Strategy
Problem: Generic content not targeting local search terms.
Solution:
- Create location-specific service pages
- Include city and region names naturally in content
- Write locally-relevant blog content (local events, community involvement, local industry news)
- Create content for “near me” searches
- Add location schema markup to all pages
Local Link Building
Problem: Backlinks from national sites don’t boost local rankings as effectively as local links.
Solution:
- Partner with local businesses for cross-promotion and links
- Sponsor local events or organizations
- Join local business associations and chambers of commerce
- Get featured in local news and publications
- Build relationships with local bloggers and influencers
Review Management
Problem: Few reviews or many negative reviews without responses.
Solution:
- Ask satisfied customers for reviews
- Make the review process easy (direct links)
- Respond to all reviews, positive and negative
- Address negative reviews professionally and offer solutions
- Never buy fake reviews (Google penalizes this severely)
- Monitor review sites regularly
12. Content Quality and Optimization
Content quality is the foundation of all SEO success. Without genuinely valuable content, no amount of technical optimization or link building will achieve sustainable rankings.
What Makes High-Quality Content?
Comprehensive Coverage: Content thoroughly addresses the topic, answering main questions and related queries users might have.
Originality: Unique insights, original research, or distinctive perspectives—not just rehashed information from competitors.
Accuracy: Factually correct information with proper citations and attributions.
Readability: Well-structured, scannable content with clear headers, short paragraphs, and visual breaks.
Actionability: Practical advice users can implement, not just theoretical knowledge.
Freshness: Up-to-date information reflecting current best practices and trends.
Content Depth vs Thin Content
Problem: Publishing short, shallow articles that don’t satisfy user intent.
Solution:
- Informational content: 1,500-3,000 words minimum
- Pillar content: 3,000-6,000 words
- Supporting content: 800-1,500 words
- Depth matters more than length: Better to write 2,000 comprehensive words than 5,000 words of fluff
Content Freshness Strategy
Problem: Publishing content once and never updating it, allowing information to become outdated.
Solution:
- Review top-performing content quarterly
- Update statistics and examples
- Add new sections addressing emerging trends
- Remove outdated information
- Update publication date to signal freshness
- Expand thin content with new insights
Multi-Format Content
Problem: Text-only content limits engagement and accessibility.
Solution:
- Add relevant images to break up text
- Create custom diagrams and infographics
- Embed videos when they add value
- Include downloadable resources (templates, checklists, guides)
- Use tables to present data comparatively
- Add interactive elements when appropriate
Featured Snippet Optimization
Problem: Competitors occupy featured snippets for your target keywords.
Solution:
- Identify keywords where featured snippets appear
- Format content to match snippet type:
- Paragraph snippets: Direct 40-60 word answer immediately following a question header
- List snippets: Use numbered or bulleted lists with a clear structure
- Table snippets: Present comparative data in HTML tables
- Include the question as an H2 or H3
- Provide clear, concise answers
- Use schema markup (FAQ, How-to) to increase chances
13. Analytics and Performance Tracking
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Effective SEO Strategy requires continuous monitoring and data-driven optimization.
Essential SEO Metrics
Organic Traffic: Total visitors from search engines
- Track overall trends and seasonal patterns
- Segment by landing page to identify top performers
- Monitor traffic quality (bounce rate, time on page)
Keyword Rankings: Position in search results for target keywords
- Track primary keywords weekly
- Monitor long-tail keyword performance
- Identify ranking opportunities (positions 11-20 with optimization potential)
Click-Through Rate (CTR): Percentage of impressions that result in clicks
- Monitor in Google Search Console
- Low CTR despite good rankings indicates title/meta description optimization needed
- Average CTR by position: #1 = 28%, #2 = 15%, #3 = 11%
Backlink Profile: Quality and quantity of inbound links
- Track total backlinks and referring domains
- Monitor link quality (authority, relevance)
- Identify and disavow toxic links
Core Web Vitals: Page experience metrics
- LCP, INP, CLS scores from Google Search Console
- Monitor failing pages and prioritize fixes
- Track improvements after optimization
Conversions from Organic Search: Ultimate success metric
- Track goal completions from organic traffic
- Calculate the conversion rate by landing page
- Measure the ROI of SEO efforts
Essential SEO Tools
Google Search Console (Free): Must-have for every website
- Monitor indexing status and coverage issues
- Track keyword performance and CTR
- Identify Core Web Vitals issues
- Submit sitemaps and request indexing
- Monitor mobile usability
Google Analytics 4 (Free): Traffic and user behavior analysis
- Track organic traffic sources
- Analyze user engagement metrics
- Set up conversion tracking
- Create custom reports for SEO metrics
- Segment data by landing page and user behavior
Keyword Research Tools:
- Ahrefs: Comprehensive SEO Strategy toolset (keyword research, backlink analysis, rank tracking, competitor analysis)
- SEMrush: All-in-one marketing toolkit
- Moz: Beginner-friendly SEO platform
- Google Keyword Planner: Free basic keyword data
Technical SEO Tools:
- Screaming Frog: Website crawler for technical audits
- PageSpeed Insights: Performance and Core Web Vitals analysis
- GTmetrix: Page speed testing and optimization recommendations
Rank Tracking:
- Ahrefs Rank Tracker
- SEMrush Position Tracking
- SERPWatcher (Mangools)
Regular SEO Audit Checklist
Monthly Tasks:
- Review Google Search Console for new errors
- Check Core Web Vitals performance
- Monitor keyword rankings for significant changes
- Analyze top-performing content
- Review and respond to new backlinks
Quarterly Tasks:
- Comprehensive technical SEO audit
- Content performance review and update plan
- Competitor analysis
- Backlink profile audit
- Conversion Rate Optimization analysis
Annual Tasks:
- Complete SEO strategy review
- Industry trends analysis and strategy adjustment
- Tool evaluation and potential changes
- Major site architecture review
14. Common SEO Problems and Solutions
Problem 1: “I’m creating content but not ranking.”
Diagnosis:
- Content doesn’t match search intent
- Insufficient topical authority
- Weak E-E-A-T signals
- Technical issues are blocking indexing
Solution:
- Analyze SERP results for target keywords and match content format
- Build content clusters around core topics
- Add author credentials and expertise signals
- Check Google Search Console for indexing issues
Problem 2: “My rankings dropped suddenly.”
Diagnosis:
- Google algorithm update
- Technical issues (site speed, mobile usability)
- Manual penalty or security issue
- Competitors improved their content
Solution:
- Check Google Search Console for manual actions
- Review the algorithm update history for timing correlation
- Audit technical SEO Strategy using Screaming Frog
- Analyze competitor content improvements
- Review the backlink profile for toxic links
Problem 3: “High traffic but low conversions.”
Diagnosis:
- Attracting the wrong audience (keyword intent mismatch)
- Poor landing page optimization
- Slow page speed is causing abandonment
- Weak calls-to-action
Solution:
- Review keyword intent and align content
- Optimize landing pages for conversion (clear CTAs, trust signals, reduced friction)
- Improve page speed (compress images, minimize scripts)
- A/B test different conversion elements
Problem 4: “Can’t compete with high-authority sites.”
Diagnosis:
- Targeting overly competitive keywords
- Insufficient differentiation
- Weak backlink profile
Solution:
- Narrow topic focus to less competitive niches
- Target long-tail keywords that competitors ignore
- Create superior, more comprehensive content
- Build topical authority in a specific subtopic
- Earn relevant backlinks through linkable assets
Problem 5: “My site is slow, and I don’t know why.“
Diagnosis:
- Large uncompressed images
- Too many plugins or scripts
- Poor hosting
- No caching
Solution:
- Use PageSpeed Insights to identify specific issues
- Compress all images (use WebP format)
- Remove unnecessary plugins
- Implement caching plugin (WP Rocket, W3 Total Cache)
- Consider upgrading hosting or using a CDN
Problem 6: “Google isn’t indexing my pages.”
Diagnosis:
- Robots.txt blocking crawlers
- Noindex tags on pages
- Duplicate content
- Low-quality content flagged
Solution:
- Check the robots.txt file for blocks
- Review the page source for noindex tags
- Ensure unique, valuable content
- Submit URL for indexing in Google Search Console
- Check for crawl errors in Search Console
15. 12-Month SEO Implementation Roadmap
Month 1-2: Foundation and Audit
Week 1-2:
- Set up Google Search Console and Analytics 4
- Conduct a comprehensive technical SEO audit
- Identify and document critical issues
- Set baseline metrics for tracking
3-4:
- Fix critical technical issues (crawl errors, mobile usability, Core Web Vitals)
- Optimize site architecture and navigation
- Set up an XML sitemap and submit to search engines
- Implement schema markup basics
5-8:
- Conduct thorough keyword research
- Analyze competitor strategies
- Define topical focus and content clusters
- Create a detailed content calendar
Expected Results: Technical foundation solid, clear strategy documented, critical issues resolved.
Month 3-4: Content Foundation
Week 9-12:
- Write and publish pillar content (comprehensive guide)
- Create 4-6 tier-2 cluster articles
- Implement internal linking structure
- Optimize all content for on-page SEO Strategy
Week 13-16:
- Continue cluster content production (4-6 additional articles)
- Add author bios and E-E-A-T signals
- Optimize images and implement alt text
- Create FAQ sections for existing content
Expected Results: Core content cluster established, 10-15 high-quality articles published, internal linking framework in place.
Month 5-6: Authority Building
Week 17-20:
- Continue regular content publication (4-6 articles monthly)
- Create first linkable asset (original research, comprehensive guide, or tool)
- Begin guest posting outreach
- Optimize Google Business Profile (if applicable)
Week 21-24:
- Launch link-building campaigns
- Engage in industry forums and communities
- Respond to journalist requests (HARO)
- Build local citations (if applicable)
Expected Results: 20-25 published articles, initial backlinks acquired, topical authority developing, beginning to rank for long-tail keywords.
Month 7-8: Expansion and Optimization
Week 25-28:
- Expand content clusters with supporting articles
- Update and refresh top-performing content
- Continue link-building efforts
- Monitor and respond to reviews
Week 29-32:
- Analyze ranking data and identify quick wins
- Optimize underperforming pages
- Create a second linkable asset
- Strengthen internal linking
Expected Results: 30-35 total articles, improved rankings for multiple keywords, steady backlink growth, and increased organic traffic.
Month 9-10: Advanced Strategies
Week 33-36:
- Implement advanced schema markup
- Optimize for featured snippets
- Create video or multimedia content
- Focus on GEO optimization for AI search
Week 37-40:
- Conduct mid-year performance review
- Identify content gaps and opportunities
- Scale content production if resources allow
- Pursue high-authority backlink opportunities
Expected Results: 40-45 articles published, ranking for competitive keywords, featured snippets acquired, strong topical authority signals.
Month 11-12: Scaling and Refinement
Week 41-44:
- Continue consistent content production
- Update older content with fresh information
- Analyze conversion paths and optimize
- Strengthen E-E-A-T signals across the site
Week 45-48:
- Conduct a year-end comprehensive audit
- Document wins, and lessons learned
- Plan next year’s strategy based on performance
- Celebrate achievements and set new goals
Expected Results: 50-60 articles in content ecosystem, established topical authority, strong rankings across keyword spectrum, measurable ROI from SEO Strategy efforts.
Ongoing Maintenance (After Month 12)
Weekly:
- Monitor Google Search Console for errors
- Publish 1-2 new articles
- Respond to comments and reviews
Monthly:
- Track keyword rankings and traffic
- Review Core Web Vitals
- Conduct link-building outreach
- Update 2-3 existing articles
Quarterly:
- Comprehensive performance review
- Competitor analysis
- Major content updates
- Strategy adjustments based on data
Conclusion
SEO strategy in 2026 is not about manipulating search engines—it’s about becoming the genuine authority Google wants to rank. The websites winning in search results are those that:
- Understand and match search intent at every stage of the user journey
- Build comprehensive topical authority through interconnected content clusters
- Demonstrate E-E-A-T signals with expert authors, original insights, and regular updates
- Maintain strong technical foundations with fast, mobile-friendly, crawlable websites
- Earn quality backlinks from relevant, authoritative sources
- Optimize for AI search to capture citations in generative AI answers
- Use semantic SEO Strategy to show understanding of entity relationships and topic depth
The most common mistake is trying to rank for everything. Instead, choose a narrow topic you can dominate, cover it comprehensively, and expand from that foundation of authority.
Start with the 12-month roadmap outlined above. Months 1-2 focus on fixing technical issues and planning. Month 3-6 builds your content foundation. Month 7-12 scales your authority and refines based on data.
Success requires patience—meaningful results typically appear after 6-9 months of consistent effort. But unlike paid advertising, SEO compounds over time. Content you create today continues generating traffic for years.
The websites that will succeed in 2026 and beyond are those that provide genuine value, demonstrate real expertise, and earn trust through consistent quality. Build your SEO strategy on these principles, follow this roadmap systematically, and you’ll position your website for long-term ranking success.
Faqs
In 2026, the most crucial factor is building topical authority. Google prefers websites that cover topics comprehensively, show expertise, and provide trustworthy information.
Implement Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) by providing clear answers, structured data (FAQ, How-to schema), and comprehensive content clusters to get cited in AI-generated results.
Common issues include mismatched search intent, weak E-E-A-T signals, thin content coverage, technical SEO problems, or ignoring AI and semantic SEO opportunities.
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) helps Google determine your credibility. Use author bios, accurate data, original insights, and backlinks from reputable sources.
Content clusters demonstrate topical authority by interlinking a pillar page with detailed subtopic articles. This shows Google that your site is a comprehensive resource for a topic.
Issues like slow page speed, crawl errors, poor mobile usability, missing schema, and broken internal links prevent Google from indexing and ranking your content effectively.
SEO results typically appear 6–9 months after consistent implementation. Unlike paid ads, SEO compounds over time, providing long-term traffic and authority growth.

